Description
What Is Flubromazolam?
Flubromazolam is an extremely potent synthetic benzodiazepine belonging to the triazolobenzodiazepine subclass. It first appeared on the research chemical market around 2014 and quickly gained attention due to its powerful sedative and amnesic effects.
Unlike prescription benzodiazepines such as diazepam (Valium) or clonazepam (Klonopin), Flubromazolam has no approved medical use. It is considered a designer drug or novel psychoactive substance (NPS) and is often sold online as a so-called “research compound.”
Chemical Profile and Pharmacology
-
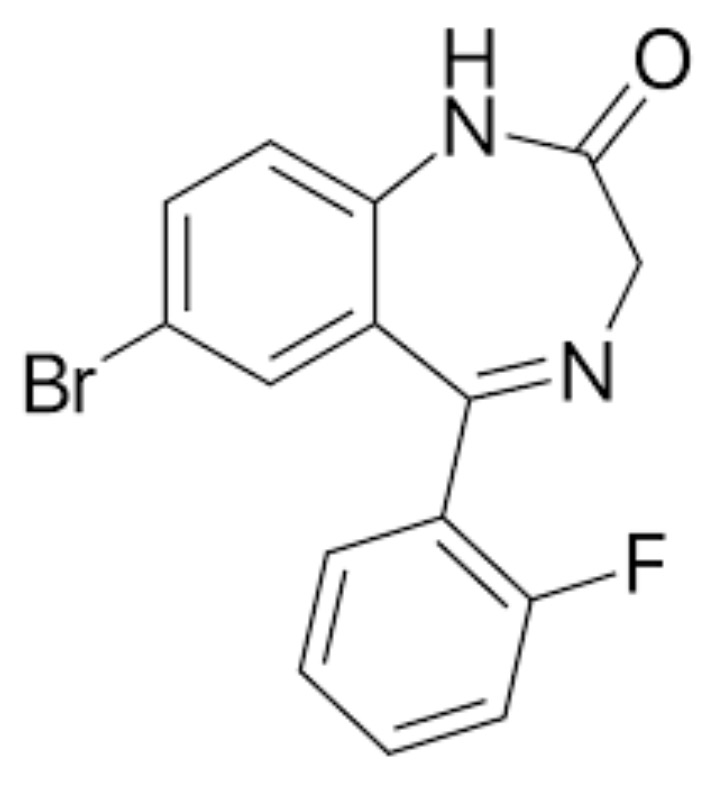
Chemical name: 8-Bromo-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]benzodiazepine
-
Drug class: Benzodiazepine analog
-
Mechanism of action: Positive allosteric modulator of GABA-A receptors
-
Molecular formula: C17H12BrFN4
Flubromazolam binds strongly to GABA-A receptors in the brain, greatly enhancing the effects of the neurotransmitter GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). This leads to sedation, anxiolysis, muscle relaxation, and memory suppression.
Effects of Flubromazolam
Because of its extraordinary potency, Flubromazolam can cause intense effects even at microgram (μg) doses.
Users have reported that as little as 0.1 mg can produce strong sedation.
Common effects:
-
Deep sedation and relaxation
-
Anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) effects
-
Muscle relaxation
-
Memory loss (anterograde amnesia)
-
Impaired coordination and motor control
-
Sleepiness lasting up to 24–48 hours
Adverse effects:
-
Confusion and blackouts
-
Slowed breathing (respiratory depression)
-
Extreme drowsiness
-
Unconsciousness
-
Risk of coma or death when combined with other depressants
Risks and Toxicity
Flubromazolam is significantly more potent than most prescription benzodiazepines. The difference between a “recreational” and a toxic dose can be extremely small — making overdose easy and often unintentional.
When combined with alcohol, opioids, or other sedatives, it can cause fatal respiratory depression. Because it is not regulated for medical use, the purity and dosage of Flubromazolam sold online are unpredictable.
Key dangers:
-
High risk of blackouts and memory loss
-
Overdose potential due to microgram-level potency
-
Severe withdrawal symptoms upon cessation
-
Physical dependence with repeated use
-
Drug interactions with other CNS depressants
Detection and Forensic Identification
Because Flubromazolam is not included in standard drug screens, detection typically requires specialized forensic toxicology techniques, including:
-
LC-MS/MS (Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry)
-
GC-MS (Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry)
-
High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS)
It is frequently identified in post-mortem toxicology reports and drug seizure analyses, often in combination with other benzodiazepines or opioids.
Dependence and Withdrawal
Regular use of Flubromazolams can lead to rapid tolerance and physical dependence.
Withdrawal symptoms may appear within hours to days after the last dose and can include:
-
Severe anxiety and panic attacks
-
Insomnia
-
Muscle tension
-
Seizures
-
Tremors and restlessness
Medical supervision is strongly recommended for anyone discontinuing use after repeated exposure.
Harm Reduction Tips
If someone encounters Flubromazolam, the following harm reduction strategies can reduce risks:
-
Avoid mixing with alcohol, opioids, or other sedatives.
-
Use accurate milligram or microgram scales if handling the substance.
-
Never use alone; have a trusted person nearby.
-
Keep flumazenil (a benzodiazepine antagonist) available in emergency settings only under professional care.
-
Seek immediate help for signs of overdose (e.g., slow breathing, unresponsiveness).
Conclusion
Flubromazolam is one of the most potent benzodiazepine analogs ever synthesized. Its unpredictable effects, long duration, and high overdose risk make it a dangerous substance with no safe recreational use.
Public awareness, accurate information, and harm reduction education are essential to prevent accidental poisonings and fatal overdoses linked to this powerful drug.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.