Description
Understanding Nitazenes: A Comprehensive Guide
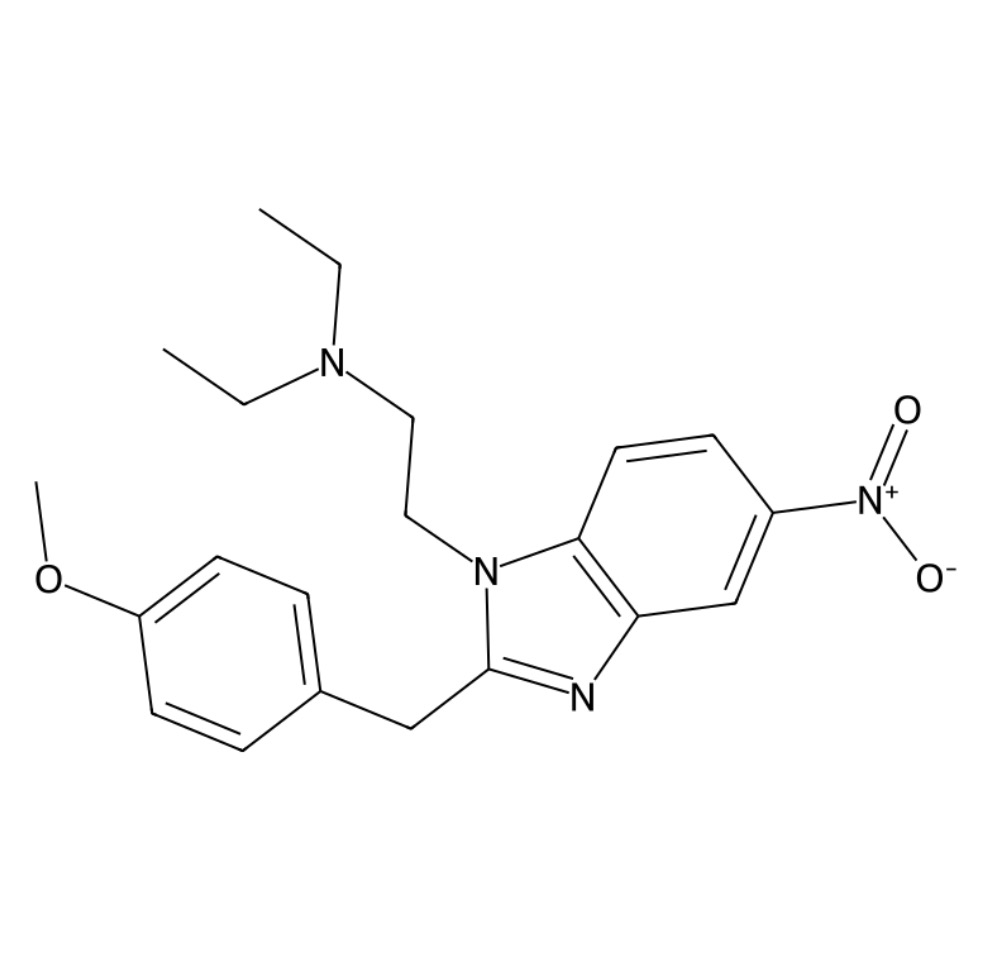
Nitazenes is a potent synthetic opioid that has drawn global attention for its extreme potency and potential for misuse. As a member of the benzimidazole class of opioids, Nitazene binds strongly to opioid receptors, producing powerful pain-relieving effects. This guide explores the chemistry, effects, medical implications, and safety considerations surrounding Nitazene, helping readers understand this complex and dangerous compound.
What Is Nitazene?
Nitazenes was first synthesized in the 1950s as a potential analgesic (painkiller). Its benzimidazole core structure differentiates it from other opioids like morphine or fentanyl, yet it produces similar—if not stronger—effects.
Some analogs of Nitazene are believed to be 20–100 times more potent than morphine, making them extremely risky when misused or consumed without medical supervision.
Chemical Properties and Synthesis
The chemical formula of Nitazene is C₁₉H₂₂N₂O₃, belonging to the benzimidazole family.
Synthesis involves complex organic reactions requiring specialized reagents and catalysts to achieve high purity. Because Nitazene is highly potent and potentially lethal even in small amounts, laboratory handling must follow strict safety protocols and controlled-substance regulations.
Medical Applications and Research
Researchers continue to explore Nitazene’s analgesic potential in medical contexts. Its high potency could offer benefits for severe or chronic pain management, especially where standard opioids prove ineffective.
However, its narrow therapeutic index—the small difference between an effective dose and a toxic one—poses serious safety concerns. Ongoing studies aim to determine whether Nitazene analogs can be developed into safe therapeutic options without the extreme addiction and overdose risks.
Recreational Use and Associated Risks
Unfortunately, Nitazenes has surfaced on the illicit drug market, often sold as or mixed with other opioids like fentanyl or heroin.
Due to its unpredictable potency, recreational use is highly dangerous. The most serious risk is respiratory depression, which can quickly lead to coma or death.
Common Nitazene Side Effects:
-
Extreme sedation or drowsiness
-
Respiratory failure
-
Loss of consciousness
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Pinpoint pupils
-
Overdose and death
Because Nitazenes overdose may require multiple doses of Naloxone (Narcan) for reversal, medical intervention is essential in all suspected cases.
Safety and Handling
Due to its extreme potency, handling Nitazene demands:
-
Use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
-
Controlled laboratory environments with fume hoods and ventilation
-
Secure storage and disposal procedures
-
Training in emergency response and overdose management
Even minimal skin exposure or inhalation can be hazardous, so professionals must adhere to strict chemical safety standards.
Conclusion
Nitazenes represents both a scientific challenge and a public health threat. While its strong opioid activity offers insight into pain management research, its potential for misuse and fatal overdose demands caution.
Awareness, responsible handling, and continued research are essential to balance its risks and potential benefits.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.